4 - Water
You can only survive at most a few days without water. Knowing how to find and purify water is vital in a survival situation.
This chapter is for informational purposes only and does not replace professional advice; use at your own risk and ensure compliance with local laws.
Be prepared
Gear
Necessities:
- Water (enough for the duration of your trip, plus a bit extra).
- Bring a water purification method for longer trips and plan your route to include water sources.
- Water containers (preferably a container that you can boil water in, such as a single-walled stainless steel bottle)
Optional:
- Water purification method (tablets or filter)
- Cooking pot or container
- Clear plastic sheet/tarp
If you don't have room for a metal container, you can pack aluminum foil, which you can form into a bowl shape in an emergency.
Knowledge and skills
Start by learning how to do the following:
- Plan your water needs for the trip
- Locate water sources
- Purify water by boiling
Once you have mastered these skills, you should learn how to do the following:
- Purify water using chemical treatment or filtration
- Collect water from plants and other sources
- Collect water using a solar still
- Boil water using hot rocks
- Desalinate water
Hydration essentials
Assume all surface water is contaminated and requires purification, and, if you have to choose a water source, try to find running water. To avoid getting sick or becoming dehydrated quickly, avoid drinking alcohol, saltwater, stagnant water, urine, or eating snow.
At 70°F (20°C), you will need around 2 to 3 quarts/liters of water daily. This amount increases with physical activity and exposure to higher temperatures.
Dehydration
Dehydration occurs when the body loses more fluids than it takes in. Symptoms include thirst, dry mouth and throat, fatigue, dizziness, dark urine, reduced urine output, dry skin, headache, and confusion.
Finding water
You can find water in many places if you know where to look. Unless otherwise stated, you should purify all water that you collect.
Precipitation
Rainwater collected directly in clean containers does not need purification, but it should be purified if it has touched another surface. Snow and ice should be melted using a fire or body heat before drinking; eating it directly can lower your core body temperature.
Bodies of water
Flowing water from rivers or streams is typically safer than lakes, ponds, and stagnant water. Saltwater can be put into a solar still to remove the salt and should never be consumed directly.
Groundwater
Water is available in many places by just digging a hole in the ground and allowing water to seep in. You can find groundwater in dry environments by looking for green vegetation, valleys, low areas, or dry riverbeds.
Plants
Plants can provide water when no open sources are available. Look for green bamboo, vines, or coconuts for easy access to water, but be sure to positively identify the plant before consuming. You can extract water from other plants by placing them into a solar still.
Dew can be collected from plants in the early morning using a cloth or piece of clothing to soak up the water. Only collect dew from plants you can positively identify as safe (non-toxic).
Solar stills
Solar stills produce small amounts of water and are best used as a supplement.
Below-ground solar still
A below-ground solar still is a simple device that uses the sun's heat to draw moisture from the soil or plants. The moisture then condenses on a plastic sheet and can be collected in a container.
- Dig a bowl-shaped hole about 3 feet (1 meter) across and 2 feet (0.6 meters) deep. Ensure it is in direct sunlight.
- Place a container in the center of the hole. Optionally, place plants or water around the container to increase moisture (do not place them in the container). You may need to weigh down or secure the container to ensure it doesn't float if you are pouring water into the hole.
- Place a plastic sheet over the hole, securing the edges with rocks or soil. You can use a clear bag if you don't have a sheet.
- Place a small rock in the center of the sheet directly over the container.
- Wait for the sun to heat the ground and evaporate moisture, which will condense on the plastic and drip into the container.

Transpiration bag
A transpiration bag is a plastic bag tied around a leafy branch of a tree you have identified as safe (non-toxic) to collect water.
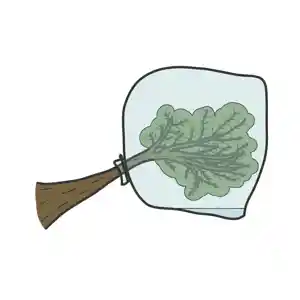
- Tie a plastic bag around a leafy branch, ensuring that the bag is airtight.
- Wait for the sun to heat the plant, causing moisture to evaporate and condense on the bag.
- Collect the water that has condensed inside the bag.
Making water safe to drink
Always ensure the water you collect is safe to drink. Boiling is the most reliable method, but chemical purification tablets and filters are also effective. If you cannot purify the water immediately, prioritize finding and storing water until you can treat it.
Boiling
Bring water to a rolling boil for at least one minute. At higher altitudes (above 6,500 ft/2,000 m), boil for three minutes. If you do not have a single-walled metal container that can be used for boiling, then do the following:
- Find another container, dig a hole in the ground and line it with a waterproof material, or craft a bowl.
- Fill the container with water.
- Heat rocks in a fire and place them in the water to heat it. Do not use rocks that may contain moisture (such as river rocks), as they can explode. Use two sticks in a chopstick fashion to move the rocks.
- Replace the rocks with hot ones to keep the water boiling.
Filtration
Use a portable water filter to remove contaminants. Some filters are rated to remove nearly all bacteria and can be used without additional purification. Custom-crafted filters are less effective and require additional purification.
A filter will have an inlet and an outlet, and it typically shows the direction of water flow with an arrow or text (inlet to outlet). Place the inlet into the dirty water and the outlet into a container, then pump to filter the water. If you are using a filter straw, the inlet goes into the water and the outlet into your mouth. Be careful never to let the outlet come into contact with unfiltered water. After filtering, you can remove the inlet from the water and pump a couple of times to push out excess water. With a straw, forcefully blow into it to clear out water.
If the manufacturer's instructions are different, be sure to follow them instead.
Chemical treatment
Chemical water purification tablets or drops can be used to treat water. Be sure to follow the instructions, which are normally printed on the package. The most common chemical is iodine, but chlorine-based treatments are also available. Before deciding which to buy, research how effective they are against bacteria and parasites in your region. Treatment amounts and times vary by chemical type and brand. Be sure to check the expiration date (if any) before going on a trip.
If you are pregnant or have thyroid problems, don't use iodine. Always read the warnings on the packages of chemical purification solutions before buying them.
Here are some general steps (if you have the manufacturer's instructions, use them instead):
- Fill a bottle with water. You may want to run the water through a filter or cloth to remove sediment.
- Add the correct amount of tablets/drops and put the cap on loosely (see below for popular brands).
- Wait 5 minutes and shake. Be sure some water leaks out of the cap and around the threads.
- Tighten the cap and wait for the purification time (see below for popular brands).
- Your water is now ready to drink.
Here are some instructions taken from popular brands as of 2025:
Potable Aqua (Iodine):
- 2 tablets per liter
- Purification time: 30 minutes
- Additional instructions (optional): After waiting for the purification time, add 2 neutralizer tablets per liter, shake, and wait 3 minutes. This will help improve the taste.
Potable Aqua (Chlorine):
- 1 tablet per liter
- Purification time: 4 hours
- Additional instructions: Use an opaque container or keep the bottle in the dark.
Aquatabs (Chlorine, 49mg)
- 1 tablet per 0.75-2 liters
- Purification time: 30 minutes
- Additional instructions: Use 2 tablets if the water is dirty, cloudy, stained, or cold.
Conversions
The following conversions are approximate, but that is fine for purification.
- 1 liter = 1 quart
- 1 liter = 1000 milliliters
- 1 quart = 32 ounces
- 1 gallon = 4 quarts
Solar disinfection
As a last resort, you can use sunlight to purify water in a clear water bottle.
- Fill a clear water bottle with water. If the water is cloudy, run it through a filter or cloth first.
- Remove the label from the bottle and lay it on its side in direct sunlight. If you have something dark, place it underneath the bottle to increase its effectiveness.
- If it is sunny, most germs will be killed in 6 hours. If it is cloudy, you will need to wait 2 days - so consider using a different purification method.
Hazards
Water may contain bacteria, viruses, and parasites that can cause illness. Boiling water kills most microorganisms, but some may require additional treatment. Microorganisms are more likely to be present in stagnant water.
Water may contain chemicals from industrial or agricultural runoff. Purification methods may not remove all chemical contaminants. Avoid drinking water next to roads, farms, or other inhabited areas.
There may be terrain or wildlife hazards present at water sources; always be aware and cautious. Avoid slippery areas, loose rocks, or patches of soft ground while gathering water.
Craft: Bowl
A wooden bowl can be used to boil water using hot rocks.

Resources
- A small log (not decayed)
- Hot coals
Instructions
- Cut or obtain a small log.
- Place hot coals into the log using makeshift tongs.
- Let the coals burn out. You can speed this up by blowing gently on the point where the coal touches the log and holding it in place with a stick.
- Scrape out the charred wood with a stick or rock.
- Repeat the process until you have a bowl.
Craft: Tongs
You can use tongs to move around hot coals or rocks without getting burned.

Resources
- Green (live) wood
Instructions
- Cut a length of green wood.
- Split the wood down the middle to create a flat surface.
- Optionally, carve a small notch in the stick's center to allow it to bend more easily.
- Bend the wood in half to create tongs. If the wood is not bending easily, either remove more material or heat the section you want to bend over a fire (do not burn it) and try again.
Craft: Filter
A crafted filter can be used to remove sediment from water, but it will still require additional purification.

Resources
- Small gravel or grass
- Sand
- Charcoal
- Plastic water bottle or container
- A second container
- (Optional) Cloth
- (Optional) Cordage
Instructions
- If using a water bottle, cut off the bottom and remove the cap. You will be using the bottle upside down.
- Tie a cloth onto the top of the bottle. If you choose not to use a cloth, poke holes in the cap and screw it back on. If using a container like a cup, poke holes in the bottom, then add some grass or rocks to the container.
- Add 1 inch (2.5 cm) of crushed charcoal to the container.
- Add 1 inch (2.5 cm) of sand to the container.
- Add 1 inch (2.5 cm) of gravel or grass to the container.
- Repeat steps 3-5 until the materials reach about 2 inches (5 cm) from the top of the container.
- Pour water into the filter and collect it in a second container.
- Purify the filtered water by boiling or using chemical treatment.